“`html
Top 5 Practical Ways to Calculate the Area of a Pyramid
The area of a pyramid is an essential concept in geometry that is applicable in various fields, from architecture to mathematics. Knowing how to effectively calculate the area not only enhances your understanding of geometric principles but also aids in real-world applications. Below we explore five practical methods to determine the area of different types of pyramids, including square, rectangular, and triangular pyramids.
Understanding Pyramid Geometry
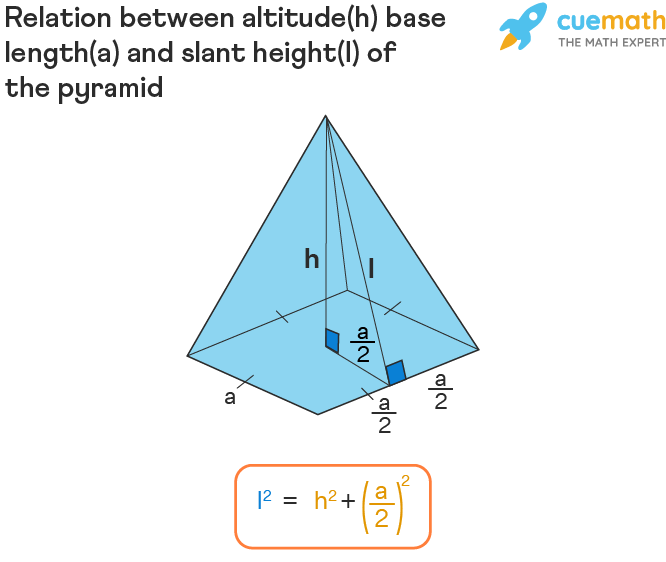
The geometry of a pyramid involves several components, including the base area, height, and slant height. Whether dealing with a triangular pyramid or a square pyramid, understanding these dimensions is crucial for accurate calculations. The pyramid height is the vertical distance from the apex to the center of the base, which plays an essential role in determining both the surface area and the pyramid volume.
Calculating the Base Area
The first step in calculating the area of a pyramid is determining the base area. Depending on the type of pyramid, the formula for the pyramid base area will vary. For a square pyramid, the area can be calculated using the formula:
Base Area = Side Length × Side Length
For instance, if the side length of the base is 4 units, the area would be:
Base Area = 4 × 4 = 16 square units.
For a rectangular pyramid, the area can be calculated as:
Base Area = Length × Width
Understanding how to calculate these base areas allows for accurate pyramidal structure designs, from simple prisms to complex geometric forms.
Utilizing the Slant Height
To calculate the lateral surface area of a pyramid, we utilize the slant height. The formula for lateral surface area is:
Lateral Surface Area = 1/2 × Perimeter of Base × Slant Height
For example, if a square pyramid has a base perimeter of 16 units and a slant height of 5 units, the calculation would be:
Lateral Surface Area = 1/2 × 16 × 5 = 40 square units.
Knowing the lateral surface area not only enhances your ability to determine total surface area but is also practical in construction and architectural design where finishes and materials are applied.
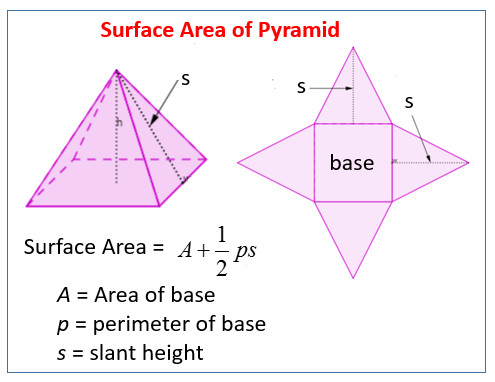
Calculating Total Surface Area
The total surface area of a pyramid combines both the base area and the lateral surface area. Understanding this is key for applications in design and architecture, as it helps assess the amount of material needed to construct a pyramid shape.
Formula for Surface Area Calculation
The formula for total surface area is straightforward:
Total Surface Area = Base Area + Lateral Surface Area
For the square pyramid from earlier, if the base area is 16 square units and the lateral surface area is 40 square units, the calculation for the total surface area will be:
Total Surface Area = 16 + 40 = 56 square units.
This comprehensive understanding allows designers to create more efficient structures, considering materials and spatial allocations.
Real-World Examples of Calculating Pyramid Area
Whether you’re teaching geometry or working in architectural design, concrete examples of area calculations are invaluable. For instance, the pyramids of Giza can be used to showcase how ancient civilizations utilized their understanding of pyramid dimensions in construction. When teaching students or clients about area calculation methods for pyramids, use visuals and models to emphasize the method’s practicality.
Applications of Pyramid Area in Various Fields
The calculations surrounding the surface area of a pyramid have powerful implications in numerous fields. From architecture to mathematics, the understanding of pyramid properties aids in project design, volume estimation, and surface area applications such as art installations and environmental design.
Architectural Designs and Pyramids
Pyramids are often seen in architectural designs, from historical structures to modern forms. When creating a structure that imitates or incorporates pyramid shapes, calculating the height of a pyramid and its area ensures stability and aesthetic appeal.
For example, consider designing an outdoor pyramid structure for educational purposes or art installations. Precise calculations facilitate effective space utilization and enhance visual impact.
Educational Perspectives on Pyramid Geometry
In schools, using real-life pyramids helps engage students. Integration of geometric properties of pyramids in the curriculum fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Workshops and interactive geometry tools can also encourage learners to visualize and understand complex geometric designs effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the various bases & heights is critical for calculating the area and volume of pyramids.
- The lateral surface area can be calculated using slant height and base perimeter.
- Total surface area combines both base and lateral areas for comprehensive design considerations.
- Real-world applications, particularly in architecture and education, significantly enhance the learning process.
FAQ
1. What is the formula for calculating the volume of a pyramid?
The pyramid volume formula is effective for all pyramid types: Volume = (1/3) × Base Area × Height. This highlights how tall structures with broad bases can carry substantial volumes.
2. How does the base shape affect the area calculation?
Different base shapes alter the formulas you might use. For a square pyramid, simpler formulas apply than for triangular bases; understanding these helps in both academic and practical applications.
3. Are there varied methods for area measurement techniques?
Yes! Using methods like geometric modeling or approximation can yield accurate results depending on the complexity of the dimensions involved in the pyramid.
4. What are the characteristics that differentiate a right pyramid from an oblique pyramid?
A right pyramid has its apex aligned vertically above the center of the base, while an oblique pyramid has its apex offset. These defining features influence area calculations and applications significantly.
5. Why are pyramids important in architecture?
Pyramids offer structural integrity due to their shape, which allows for efficient load distribution. They have historical significance in various cultures, reflected modern designs, and architectural advancements.
“`